Controllers -- What they are???
Controllers are the one of the most essential concept of WebDynpro Component. Or You can say that Controllers are all in all of any WebDynpro Component. Without Controller you can't think about WebDynpro Component.
From below diagram hope you can understand the basic concept of Controller.
As you can see the diagram. A controller is something where you will implement the your logic as well there is data storage area to storage data which you will use in your implementations
So In more precise way..
Controllers are used to handle application functionality. Various controllers exist as part of the WebDynpro framework to handle different aspects of the flow logic and WebDynpro component functionality. Programming within controllers is done via methods that refer to data stored in the context (Hierarchical Data Tree) or attributes.
Controllers are essentially ABAP classes with predefined methods, attributes and events that handle the basic functionality required based on the controller type.
Examples of the standard functionalities are:
Types of Controller:
There are different types of Controller in WebDynpro framework which are
- Component Controller
- Custom Controller
- Interface Controller
- View Controller
- Window Controller
Before going further to know more about the Controllers. Let us know something about different types of interfaces that are created at the time of component creations. These interfaces are as below.
IF_<ControllerName>
IG_<ControllerName>
IWCI_<ComponentName>
The interface begin with the prefix
IF is local and can be used for coding only
within that controller.
The interface begin with the prefix
IG is used for
Cross Controller Communication.(e.g Component controller to View Controller)
The interface begin with the prefix
IWCI is used for
Cross Component Communication.
(e.g. ComponentA to ComponentB ) Now lets come to the Controller types..
Component Controller
This is the parent controller for the WebDynpro component. There is only one Component Controller exists as per WebDynpro component and it is G
lobal Controller. i.e Component Controller consist of data, flow logic, Events, Methods are available to all the other types of controller.
This controller does not have any visual interface. The life time of the component controller is the life time of the component.
Components of Component controller:
The Properties tab consists of the description and the development attributes. It also has a
Used Controllers/Components directory. If the controller needs to share data with another controller, it must be added to this list and thus declared explicitly.

Context is a hierarchical form of storage of data. Context is a place where you declare the data. The Nodes declared here can be mapped to any no of view and can be accessed from there hence making the data of the component controller global.
Note: In Coming post you will be understand about Context and its properties.

The attributes required by the Component Controller are declared in the Attributes and are accessible to the methods of the Component Controller using the handle provided for the Component Controller (WD_THIS). The attribute
WD_THIS declared in any controller refers to the interface of the
current controller and the attribute
WD_CONTEXT refers to the corresponding C
ontext of the controller.
These attributes can also be accessed from different controllers as well using the handle provided for the Component Controller (WD_COMP_CONTROLLER) in the respective controller.

Events created in the Component Controller are visible only within the component which means it can only be triggered by the methods of the Component Controller. But it can be handled in different controllers. Thus Events are used to communicate between the controllers and enable one Controller to trigger the event and handler the event in different controller.
Events can also implement Cross Component Communication provided that the interface check box is checked.
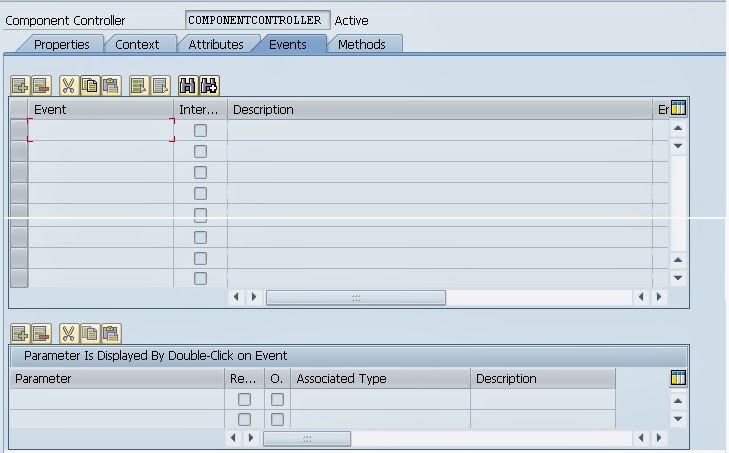
Component Controller consist of number of predefined methods called
Hook Methods which are executed in a pre-defined manner. You can also create your own methods and the methods which you created can be called from any Controller using the handle for the Component Controller (WD_COMP_CONTROLLER).
Note:- In coming post you will come to know more about Hook Methods
 Custom Controller
Custom Controller
Custom Controllers can be additionally created in the component and there are exactly similar to the Component Controller in terms of functionality. This means it is visible to all the Controllers. And life time of the controller is the lifetime of the component.
Any number of custom controller you can create in the component and it will provide you the option of structuring the data’s and functions. It only make sense to create a custom controller if certain function and data’s are to be associated with the specific set of views.
Components of Custom Controller:
The Components of Custom Controller,
Properties, Context, Attributes are similar to the Component Controller. And only
Events and
Methods are differ from Component Controller.
You can create Events and implement in a similar way to the Component Controller except that you cannot implement Cross Component Communication. It can be handled only within the component.

Unlike Component Controller the Custom Controller does not contain a no of Hook Methods. There are only two Hook Methods are available (As you can see in below screen). You can create your own methods in the Custom Controller and these methods can be used by any views provided that the Custom Controller is added to the Used Controller/Components in the properties tab of the view.
 Interface Controller
Interface Controller
Interface controller is used for
Cross Component Communication. Interface controller itself does not contain any implementation. It is the point of contact of communication for other component to use this component. Only nodes, methods and events marked as interfaces can be used by other Components.
For the Interface Controller of a Web Dynpro Controller, the methods are implemented in the related component controller.
For the Interface Controller of a Component Interface definition, the implementation is performed in the Component Controller of the embedding component.
For every interface controller there is a related ABAP interface
IWCI_<component_name> or IWCI_<Comp.Interf.Def-Name>
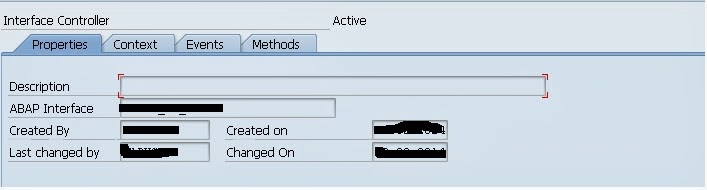
Components of Interface Controller:
In the Properties tab you will be able to see the administration data and ABAP Interface that was created for the external communication (IWCI).
In the context tab you will be able to see the context nodes of the
Component Controller which is marked as
interface node in the node properties of the Component Controller.

In the events tab you will be able to see the events which are marked as interface events for Cross Component implementation.

In the methods tab, you will be able to see the interface methods that can be accessed by the other components.
 View Controller
View Controller
No of View Controllers in a component depends upon the no of views. The view controller cares about the view specific flow logic like checking user input, handling user actions etc & design the UI using standard UI's element. The lifetime of the view controller is restricted to the life time of the view.
Components of Interface Controller:
The properties tab of the view controller consist of the admin data as well as the option to add the used controllers for the view.
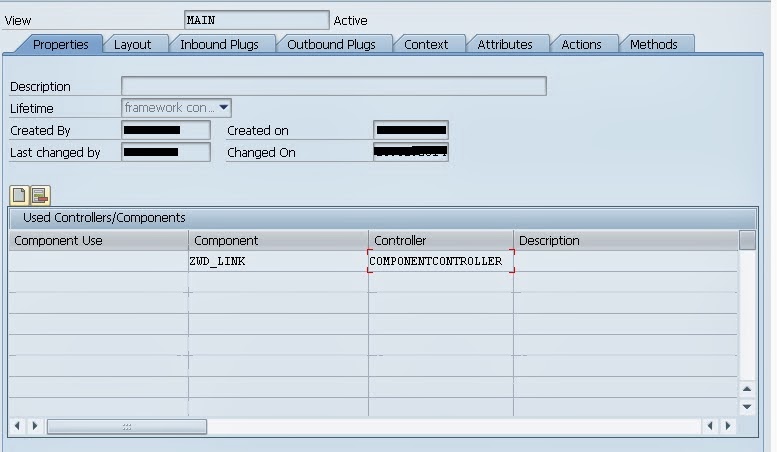
As you can see in the above screen. A component ZWD_LINK is used in view controller so you can access the methods or context data from the view controller of Component Controller. This component will be added automatically when first time you create a component. And you have to add others component in Used Controllers/Component explicitly so you able to access the functionality of other Components.
Layout is something which gives you feel as WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get). In you layout you will design the user interface using UI elements. As you can see in the below screen. Layout is divided in four parts.
UI Elements Library (left hand side)
View Design Area (middle)
UI Element hierarchy (top of right hand side)
UI Elements Properties (below of right hand side)

Plugs are required for the navigation between the views. You can create Inbound plugs here and Inbound plugs are also consist of event handler method which will be executed before displaying the view.
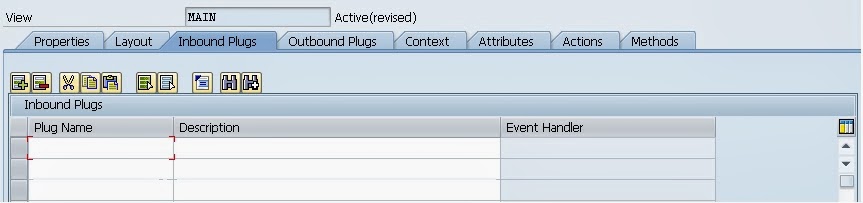
Outbound plugs consist plugs which is pointing away from the view. This does not contain any event handler method and you can define the parameters for the plugs. The Outbound Plug can be fired using following syntax.
WD_THIS->FIRE_<OutboundPlugname>_PLG( )
 Context in View Controller is same as Component Controller. You can create your Node in Context or you can use the context Node of Component Controller using Context Mapping. After Context Mapping the Context Node value of Component Controller will be visible in View Controller.
Context in View Controller is same as Component Controller. You can create your Node in Context or you can use the context Node of Component Controller using Context Mapping. After Context Mapping the Context Node value of Component Controller will be visible in View Controller.
View Controller Context is visible to the View only i.e you can not access from other controllers since View Controller doesn't allow to create interface Context.

Attributes is similar to that of the Attribute Tab as in the Component Controller. In the view controller you will be able to see the handler (WD_COMP_CONTROLLER) to the Component Controller with reference to the interface of the type IG_(Cross controller). Using this handler the attributes and methods of the component controller can be accessed.

In Action Tab all the actions will be listed for which UI Element you have created the Action and also the event handler action will be listed.

Methods Tab is similar as Component Controller. You will notice that all the Hook Methods specific to View Controller are listed apart from Hook Methods other Methods and Actions are also listed which you have created for the UI Elements.
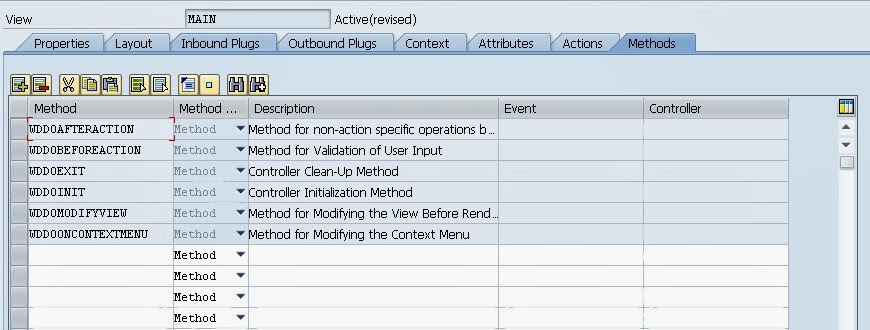 Window Controller
Window Controller
Each window in a WebDynpro component consist of a window controller. It is visible throughout the component and behaves like Component or Custom Controller.
Components of Interface Controller:
Properties tab of the Window Controller is similar to that of the View Controller.

In the window tab you will be able to see the views that are embedded in the window, inbound and outbound plug of each view and the view that is marked as default. Here you can also specify the navigation link between the views using the view plugs.
Note : Don't forget to embed the View in Window when ever you created a new View otherwise you will not able to see the view in browser.
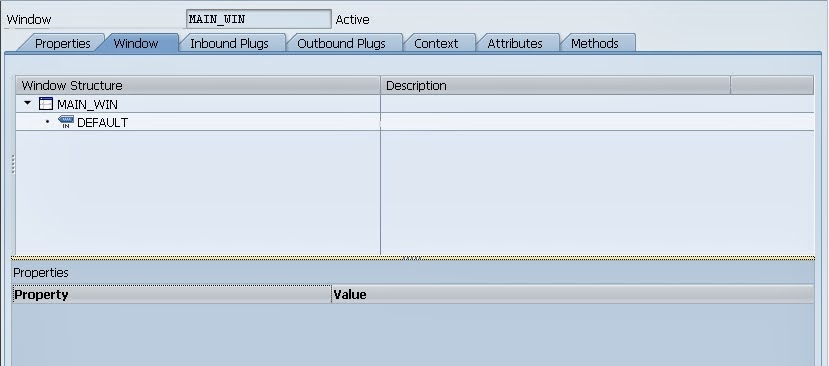
In Inbound Plugs Tab you will be able to see the one DEFAULT plug and you can define your own plugs also.
The properties of Inbound Plugs of Window is differ from Inbound Plugs of Window as different characteristic like Interface Exit, Suspend . You can create the different types of Inbound Plugs here like Startup, Exit, Resume, Suspend as well.
The
Interface Check Box determines whether the Inbound Plug is used only for navigation within the component or cross component navigation.
Outbound Plugs consist of interfaces, Exit and Suspend characteristics. And you also define the parameters for Outbound Plugs.

Window Controller can be used to implement navigation controls within the window. Typically you use it to create the data in the context that you require for navigation decisions. The context of a window controller is no different to the contexts of other global controllers; it can be viewed within the whole component

You can maintain attributes for the context of a window.

Methods Tab is similar to other controllers. You will able to see the list of Hook Methods specific to Window Controller and apart from this the event handler for inbound plugs as well as for events of other controller, you can also create the simple methods for window controller as well.

That's all about Controller. Hope you will able to understand about controllers. In coming post you will be able to understand more about Hook Methods.
And Don't forget to comment :) :)
Thanks

















































